Food or Junk Food
Where the Line Is Drawn
Not everything that is edible qualifies as food.
In modern food environments, many products are designed primarily for stimulation, shelf life, and repeat consumption — not for supporting biological function.
This page explains how we distinguish food from junk using a functional, biology-based framework rather than labels or ideology.

A Functional Model for Food Value
We evaluate food based on net biological contribution, not calories, marketing claims, or popularity.
Food Value Model
V=(NA+(TEF×PPM))−NI−C
This model is not meant to be precise to the decimal.
It is a conceptual tool to compare inputs based on how the body experiences them.
Component Descriptions
-
V (Value of Food)
The net biological value of a food after accounting for both benefits and costs. -
NA (Nutritional Absorption)
How much usable nutrition the body actually absorbs after digestion.
More absorbed nutrients = higher value. -
TEF (Thermic Effect of Food)
The energy required to digest and process food.
-Protein: high TEF (≈20–30%)
-Carbohydrates: moderate TEF (≈5–10%)
-Fat: low TEF (≈0–3%)
Foods that require more work to digest often contribute more to satiety and metabolic signaling. -
PPM (Protein Priority Multiplier)
Adjusts the importance of protein when physiological demand is higher(e.g., recovery, growth, physical stress).
This reflects the reality that protein needs are context-dependent. -
NI (Negative Impacts)
Biological stressors associated with the food, such as:
-inflammation
-glycemic spikes
-gut disruption
-metabolic stress
Higher negative impact lowers net value. -
C (Costs)
The internal resources required to repair or compensate for damage caused by the food.
Examples:
-oxidative stress repair
-detoxification
-inflammation management
High repair cost reduces long-term value.

What Qualifies as Food
Food supports biological function.
At minimum, food should:
-
provide essential nutrients
-
be biologically recognizable
-
contribute more than it costs over time
Typical characteristics of food:
-
originates from living systems
-
contains proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals
-
supports energy, repair, and regulation
Food does not need to be perfect —
it needs to be net positive.

What Qualifies as Junk
Junk is not defined by taste.
It is defined by low biological return and high interference.
Junk food typically:
-
delivers calories without meaningful nutrition
-
relies on engineered stimulation (sugar, refined fats, additives)
-
contains compounds the body did not evolve with
-
increases biological load over time
Common Junk Characteristics
-
Non-nutritive additives
Artificial flavors, colors, preservatives that provide no nutritional value. -
Engineered stability
Extended shelf life through chemical manipulation rather than freshness. -
Metabolic interference
Refined sugars, seed oils, and ultra-processed ingredients that override normal feedback signals.
Junk food is often easy to consume, hard to regulate, and costly to repair from.
What Junk Is Not
Junk is not:
-
a moral failing
-
about willpower
-
about calories alone
It is the result of engineered taste designed to bypass physiological regulation.
This is why junk aligns with the addictive taste layer, not physiological taste.
Context: The Modern Food Landscape
In the United States, a large portion of supermarket items fall into the ultra-processed category.
These products often include:
-
preservatives to extend shelf life
-
artificial flavors and colors
-
refined sugars and oils
-
ingredients optimized for consistency and cost, not compatibility
This environment makes junk the default, not the exception.
These charts are not dietary rules or medical advice.
They are visual tools illustrating how different food categories tend to interact with Homo sapiens physiology over time — particularly when consumption is frequent or habitual.
This ranking reflects a physiological perspective — prioritizing long-term compatibility and low sensory interference rather than short-term stimulation or cultural preference.
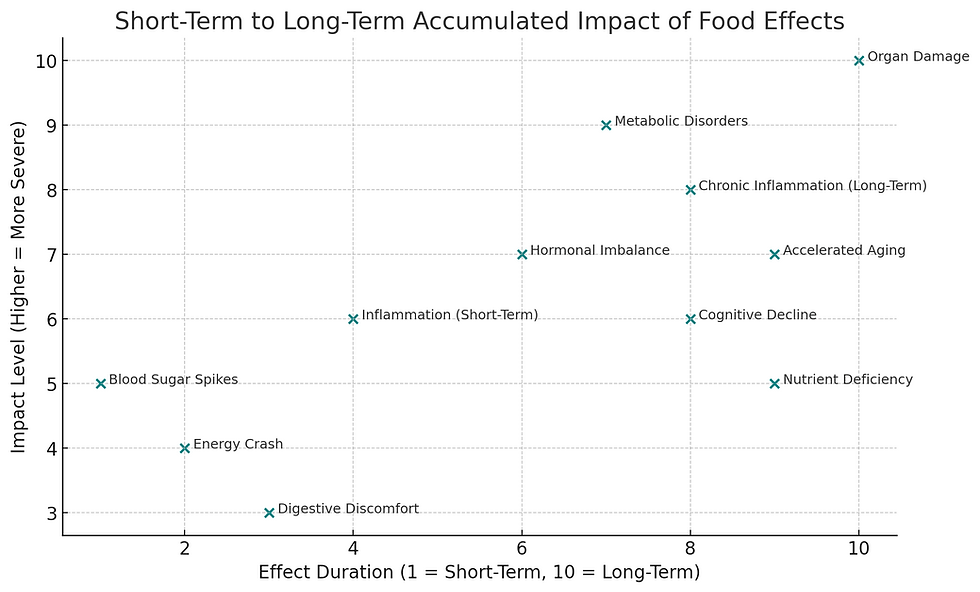
Accumulated Biological Effects of High-Stimulation Foods Over Time
This chart illustrates how certain food-related effects may feel mild or tolerable in the short term, yet accumulate into significant biological strain when exposure is frequent and long-term.
The horizontal axis represents duration of exposure.
The vertical axis represents severity of accumulated impact.
